Due to the ability of gas furnaces to heat homes quickly with forced air heating, they’ve become the preferred choice of heating system for Toronto homeowners. If you’ve ever asked yourself how does a gas furnace work, this article is for you.
Related: What Can Cause a Furnace to Stop Working?
The Basic Heating Cycle
Your furnace performs this process in cycles to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures during winter:
- The burner ignites the gas when the furnace turns on.
- The ignited flame heats the heat exchanger, and exhaust is released out the flue.
- The blower distributes warm air around your house through the system’s ductwork in exchange for cold air.
- The return air ducts suck in the dense and cold air from the surrounding forcing it back into the furnace.
- The process repeats itself, starting from the ignition to the heating, all the way to the ductwork.
 Components of Your Gas furnace
Components of Your Gas furnace
Furnace parts or components work together to achieve the desired temperature in your house. As a gas furnace owner, it can be helpful to understand the parts of a furnace and how they work. It could extend the life of your furnace. Following are the primary components of a gas furnace:
Thermostat
The function of the thermostat is to tell your furnace when to heat your home. The thermostat signals the furnace to turn on when the home’s temperature dips below the programmed temperature.
Burner
The gas furnace burners are a network of tubes and valves whereby combustion of the gas occurs. The gas ignitor, valve, and flame sensor play the role of controlling the flames. When it’s time to produce some heat, the valves open up, and the gas mixture is flamed up. The furnace’s flame sensor is responsible for gas obstruction in case a flame is absent.
Transformer
The transformer regulates the amount of electrical energy that enters the gas furnace. It increases or decreases the voltage to ensure that the furnace operates correctly.
Heat Exchanger
The heat exchanger plays an integral role in protecting homeowners from the silent killer (carbon monoxide).
When the furnace turns on, the combustion process begins. The combustion gasses (mixture of gas and combustion fumes) heat the surrounding metal walls of the heat exchanger.
The return air ducts blow cold air (drawn from inside the home) against the outside of the heat exchanger. The furnace blower then distributes the breathable heated air throughout the home via air ducts.
A venting pipe (aka flue) directs the deadly combustion gases outside your home. Venting process works slightly different in a high-efficiency furnace. Note: You must ensure that the heat exchanger is leak-free to prevent combustion gases from escaping and mixing with the breathable air.
The Plenum
There are two types of plenums; the air return plenum and the air-supply plenum. The supply plenum carries heated air and distributes it to the ductwork. Therefore, the air return plenum is responsible for transporting air from the room surrounding, through the vents, into the furnace for heating.
Flue
This part is responsible for extracting exhaust air from the combustion process. The flue carries the used gases and deposits them outside your house. SEU (Standard Efficient Units) is known to use galvanized steel. In contrast, on the other hand, high-efficiency ones use polypropylene venting, which is relatively easy to install.
Blower
The blower is a fan in the furnace that directs the incoming air from the return air vents towards the heat exchanger. Upon heating, this air is blown and forced across your home’s ductwork. Most furnaces have an inbuilt multi-speed blower, while the higher-efficient ones have a variable speed fan. The variable-speed blowers are capable of re-adjusting during operation.
Suppose you understand how every item operates entirely. In that case, you’ll have gotten your answer to the frequently asked question ‘how does a gas furnace work?’.
 Gas Furnace Maintenance and Safety Measures
Gas Furnace Maintenance and Safety Measures
Just like other combustion-based house appliances, proper maintenance of the gas furnace is mandatory to avoid heating problems. Furnace maintenance ensures that the heating system works efficiently under safe conditions. Here are the safety measures you should keep an eye on:
- Prepare a regular maintenance and cleaning schedule with a professional.
- Install at least one CO (carbon monoxide) detector and test it regularly.
- Keep all flammable items or materials from your gas furnace to avoid accidents.
- Swap your Air filters at least once in three months during routine usage.
- Maintain your furnace’s register’s cleanliness and avoid obstructing them. Make sure to uncover two-thirds of the registers to prevent excessive heat accumulation in the gas furnace.
Final Word: How Does a Gas Furnace Work?
Understanding the various components of your gas furnace and how each one works, you are in a better position to troubleshoot your furnace when it malfunctions. Remember to keep your maintenance schedule intact to increase the efficiency of your furnace. Before we call it a day, we hope the question ‘how does a gas furnace work?‘ doesn’t puzzle you anymore. Lastly, make sure you reach out to HVAC professionals and experts for inquiries about your gas furnace’s maintenance.
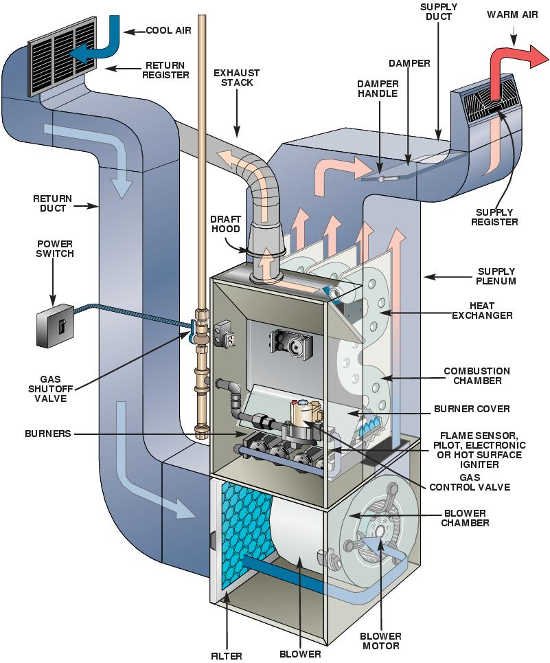 Components of Your Gas furnace
Components of Your Gas furnace  Gas Furnace Maintenance and Safety Measures
Gas Furnace Maintenance and Safety Measures